For years, marketers have relied on marketing automation services to streamline campaigns, schedule emails, and track leads. These platforms simplified routine tasks and yet it remained as a tool which can be powerful, yes, but not a decision-maker. Enter agentic AI: artificial intelligence that not only helps marketers, but has become an agent itself that can make decisions, optimize in real time, and learn new strategies without needing direct human input.
This is a transformation larger than smarter tools. had. It reflects the emergence of marketing systems that become self-strategising. To see exactly why this is important, we are going to look at it in steps.
From Automation to Autonomy
Classical marketing automation products were based on a set of pre-established rules: when a user does this, then inform them of that. That model was effective; however, it was predestined by human foresight. Someone had to envision the scenarios, develop workflows and performance monitors.
When it comes to agentic AI, things are not the same. In place of marketers dictating each step, the AI monitors the behavior and pattern of customers, reads data cues, and plans the course of action automatically. That implies less fixed flows and more marketing workflow automation that adjusts to every moment.
Think of it this way: yesterday’s automation was a chessboard with every move scripted. Agentic AI is more like an evolving game where the AI plays alongside you, learning, adjusting, and surprising you with moves you wouldn’t have considered.
What Makes Agentic AI Different
Three basic characteristics distinguish agentic AI and the conventional automation:
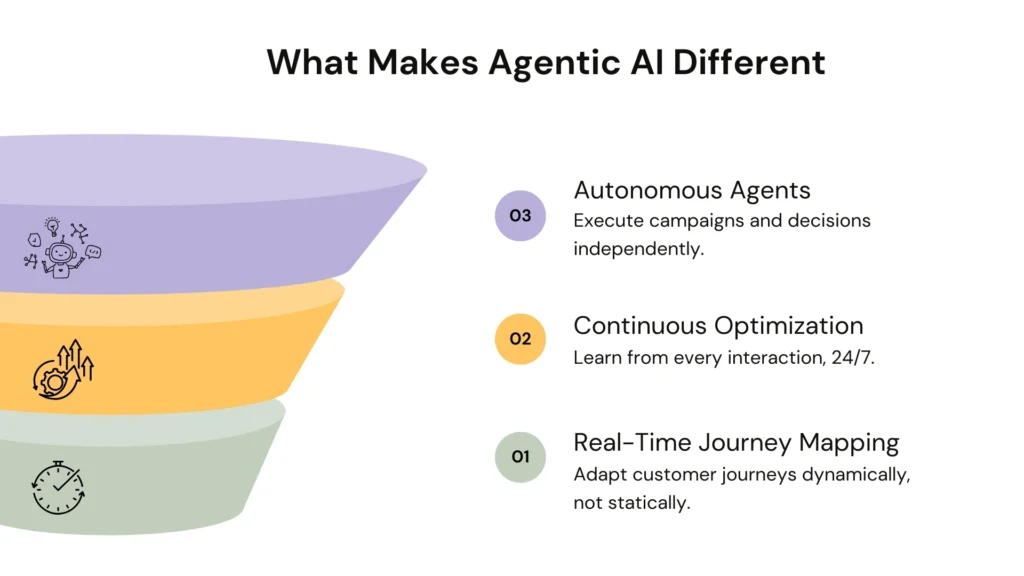
Autonomous agents: These are the systems, which not only analyze but are capable of implementing strategies. They can manage ad bidding, segment audiences, and even trigger dynamic content generation without waiting for human approval.
Continuous Optimization: In continual learning, agentic AI experiences learning by analyzing every interaction rather than waiting 3 months to review campaign performance. This gives the opportunity to quickly iterate faster than human teams.
Real-Time Journey Mapping: rule-based journeys are linear and fixed, whereas real-time journeys redefine themselves momentarily as new behavioral data comes in. In case of a sudden shift in interest by a customer between product categories of interests, the system turns immediately.
Use Cases That Go Beyond Today’s Playbooks
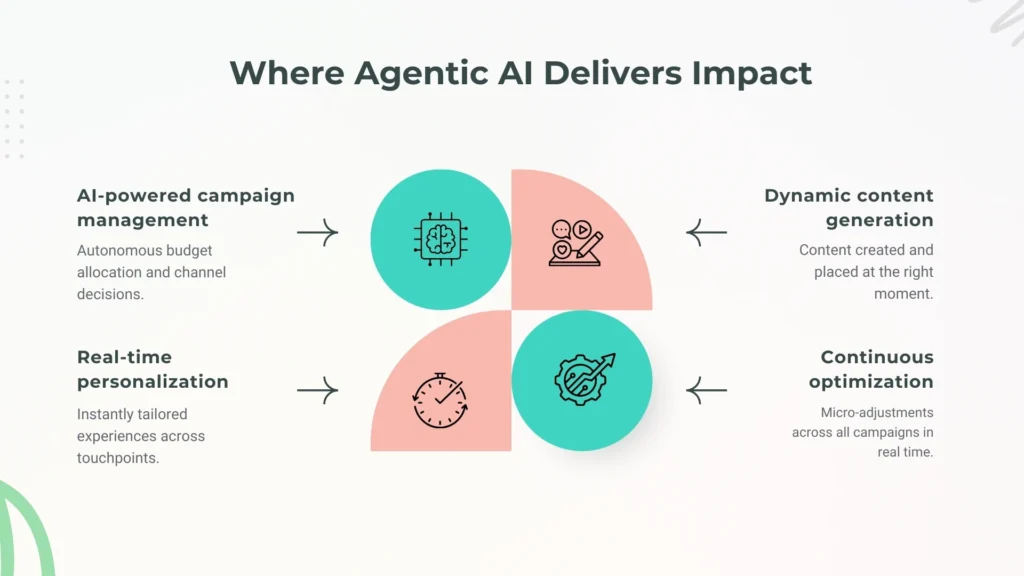
1. AI-powered campaign management
Agentic AI doesn’t just push out campaigns; it runs them end-to-end. These systems are able to make decisions on whether ads should be run, paused or change channels depending on budget allocation and being creatively tested. They are not only equalized to assistants, they are in a position to control their own campaigns.
2. Real-time personalization
Personalization has previously referred to filling in a name in the email subject line. An automated system enables real-time personalization, extracting the data on behavior such as site clicks, time on page and adding to the cart, then making adjustments to the messaging real-time. When a user spends time looking at premium products, the AI can transition between banners, mix and match copy, or even drive higher-value recommendations at the flick of a switch without a marketer ever touching a button.
3. Dynamic Content Generation
Regenerative AI goes beyond making copies with a further step. It is not only a content creator, but also an editor to preside on when and where the content should be located. This is dynamically created content as part of a more comprehensive and autonomous workflow, not an ad hoc task.
4. Continuous Optimization of multi-channel campaigns
Rather than having A/B tests take several weeks to run, continuous optimization means the system is running thousands of micro-experiments in parallel. It identifies patterns quicker and allocates resources to what is effective; be it Google Ads, LinkedIn campaigns or push notifications.
Why This Matters for Businesses
For businesses working with a marketing automation company or seeking marketing automation consultation, the rise of agentic AI raises key questions.
- How will strategy evolve when machines can handle not just execution but planning?
- What skills should marketing teams focus on if agents are taking over repetitive workflows?
- Where should oversight come in to balance autonomy with brand control?
The solution to these problems is apparent in the answers as well the new role of marketers which is they should not spend much time cogitating on email flows, instead they have to concentrate on governance, ethical limits and overall high level planning.
Informational Insights: What Teams Need to Know
Data readiness is non-negotiable
Autonomous systems feed well on good inputs. Without the support of the proper customer data (siloed, outdated, inconsistent, etc.), even the sharpest AI agent can stumble. Businesses should cleanse their CRM, CDP, and analytics stacks before through a pipeline audit in order to jump into agentic adoption.
Governance and oversight
With the decision making of autonomous agents, supervision is essential. Marketers require dashboards that are transparent: Why has the AI moved to a different section in the budget, why has the AI chosen a certain creative option over another, what criteria did it use to drive personalization? Governance does not require micromanaging, it only seeks to maintain trust and compliance.
Cost and ROI clarity
Investing in agentic AI is not purely a technology-related choice. Businesses need to consider more than the one time cost of a license, they need to consider ongoing cost reductions, higher conversion rates and faster campaign cycles. A well-defined ROI model will enable the shift in rule-based automation to autonomous operations.
Where Current Thinking Stops and Where It Needs to Go
Most discussions around AI in marketing stop at the “efficiency boost” narrative. While true, the more pressing opportunity lies in what happens after efficiency:
- Job redesign: As AI handles campaign execution, new roles emerge around oversight, AI governance, and strategic orchestration.
- Ethical frameworks: How transparent should personalization be? Should customers be informed when an AI agent, not a human, designed their experience?
- Future-proofing: As regulations around AI tighten, businesses need strategies that ensure compliance without sacrificing the agility of autonomous systems.
There are no simple answers to these questions, however, they are necessary when it comes to brands that are willing to maintain autonomy and build trust at the same time.
Connecting the Dots Across the Customer Journey
An example of agentic AI in action may be a situation such as the following:
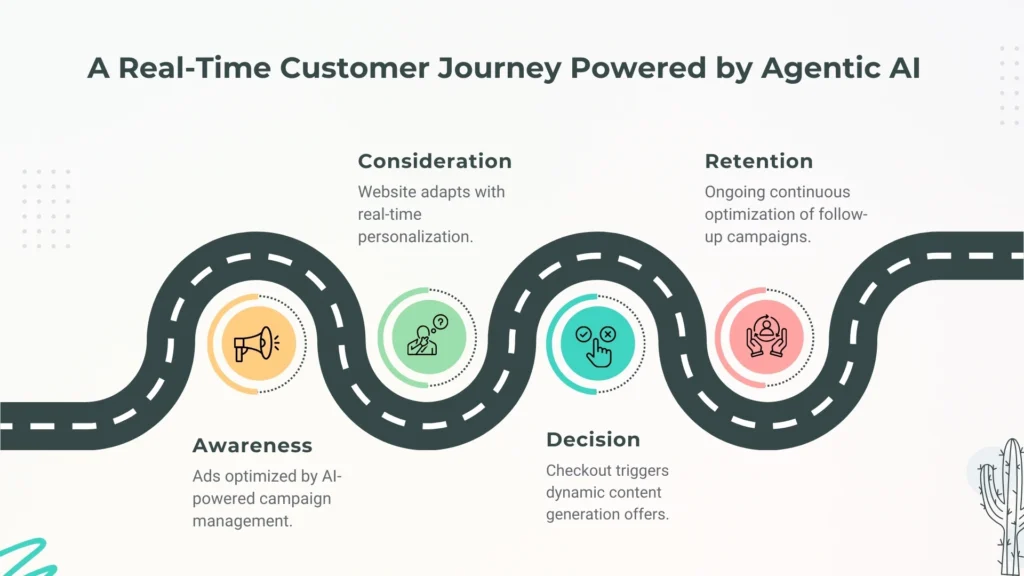
- A visitor lands on your site after seeing a paid social ad.
- The system instantly detects they’re a high-value prospect based on browsing velocity and history.
- Without waiting for a marketer’s input, the AI triggers real-time personalization by swapping homepage content to match their interest profile.
- At the same time, it has started generating dynamic content of a new email based on their behaviour.
- When the potential customer is about to abandon the cart, an autonomous agent initiates a micro-discount campaign, by performing a mini AI-powered campaign management test to determine which incentive should be applied.
- Because of the continuous optimization, efficiency is ensured as funds allocated towards campaigns that do not work are channeled to the segment of the prospect.
- All this is done quicker than a human marketer even logs in to the dashboard.
This isn’t science fiction, it’s what happens when systems move from being smart assistants to autonomous strategists.
The Bigger Picture
Companies that used the efficiency of an automated marketing service are now confronted with a new reality: namely, the tools themselves are learning how to run the playbook. An alliance between a marketing automation firm and a company is not about workflow setup anymore it is about the strategy development to control, comply, and collaborate between human and AI.
Here, marketing automation consultation will be important. Consultants are not just being asked to install software, there is more of an emphasis on data readiness, data governance, and ethical deployment.
The potential is huge on the part of marketers who come to terms with this change. As opposed to having to be in the trenches of manual optimization they become builders of smart systems systems that can learn, adapt, and optimize in ways never possible before when limited to humans alone.
FAQ’s
Traditional automated marketing follow pre-set rules. Agentic AI, on the other hand, adapts on its own, using real-time journey mapping and continuous optimization to refine campaigns.
Yes. With AI-powered campaign management, agentic systems can plan, execute, and adjust campaigns end-to-end, from budget allocation to creative testing.
Clean, unified data streams are critical. Without strong data pipelines, marketing workflow automation and agent decision-making won’t be effective.
Continuous optimization means campaigns adapt instantly, reallocating budget and adjusting messaging to maximize conversions without waiting for manual reviews.
Yes. Real-time journey mapping has a plus of dynamic adjustment of touchpoints to all businesses. The personalization that formerly was accessible to enterprise marketers is now accessible to small squads.